Related paper: SAPIEN: Affective Virtual Agents Powered by Large Language Models
Introduction
SAPIEN (Synthetic Anthropomorphic Personal Interaction ENgine) is a language model-driven coaching platform capable of engaging in open-domain conversations in real-time with users in multiple languages. This high-fidelity virtual agent platform represents a significant contribution in artificial intelligence and human-computer interaction. The project was inspired by ongoing research at the Rochester Human-Computer Interaction Lab, which involved creating virtual avatars that replicate the speech of actors portraying cancer patients to train medical students for difficult conversations. With the power of today's large language models, we realized that this technology could be easily adapted and applied to any use case that involves conversation practice.
Platform Usage
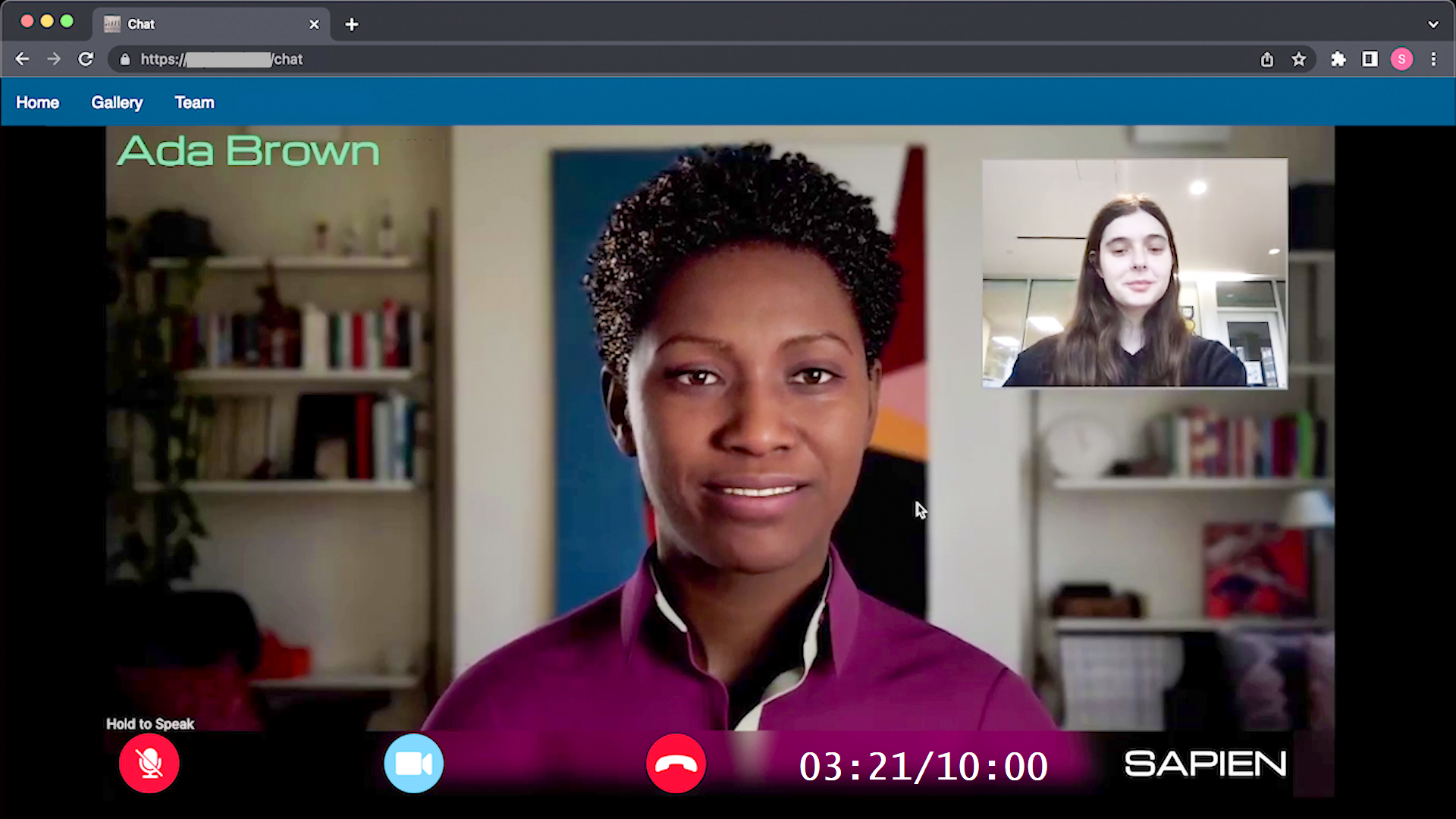
To use the platform, users navigate to the website and select a use case, such as interview practice, foreign language speaking practice, or simulating a social scenario. Based on the chosen use case, users set parameters such as the job description, resume, context of the social scenario, and the language to be practiced. Then, users can pick one of the 30+ virtual characters of varying ages, genders, and backgrounds. Once set up, the conversation begins as a video call. SAPIEN can simulate emotions reflected in the virtual agent's voice and facial expressions. Moreover, it offers users the option to personalize the virtual agent according to their preferences, including the choice of the agent's personality, background, and conversational context. I played a key role in the research team, significantly contributing to the project's development and its deployment as a website platform.
Technical Details and AI Integration
Utilizing state-of-the-art AI models, SAPIEN virtual agents provide a nuanced and immersive experience. The Speech-to-Text and Text-to-Speech models come from Microsoft Cognitive Services, ensuring high-quality audio processing. The agent fluently converses in various languages and accurately reflects emotional states. We integrated the capability of mimicking seven basic emotions such as Neutral, Happy, Sad, Angry, Surprised, Afraid, and Disgusted, which significantly enhances the interaction experience and makes it more expressive. For the chat functionality, we use GPT-3.5 for its speed and responsiveness, while GPT-4 is employed for post-conversation feedback, leveraging its superior text quality to provide detailed and insightful analysis.
Personalized Feedback and Applications
Upon concluding their interaction with the SAPIEN virtual agent, users may choose to have their conversation analysed to gain personalized feedback on their communication skills. This feedback derives from the conversation's transcript, analysed in relation to a user's specified goal. It identifies their communicative strengths and weaknesses, providing actionable recommendations for improvement. This mechanism leverages the flexibility of the virtual agent's persona and adaptability to a range of applications, including language learning, communication training, and professional applications such as healthcare, sales, and leadership training.
My Contributions and Technical Responsibilities
I contributed to the task of designing user experiences, particularly the customization of intellectual and emotional traits of AI agents, initiating dynamic conversations, and automated feedback. My responsibilities also included implementing unique features for each use case, such as an internal job search engine, a resume parser to gather user information, and temporarily capturing webcam data to infer the user's emotions for more emotionally aware conversations. Additionally, I managed the deployment on an AWS EC2 instance, as the virtual human is a MetaHuman from Unreal Engine 5 and requires significant compute power to run and scale. I also set up the Apache server to support this infrastructure. My work extended to addressing the responsible use of this technology, considering the ethical implications of such realistic virtual agent representations.
Vision and Ethical Considerations
We envisaged SAPIEN as a powerful tool designed to help people adapt by fostering human skills through AI. SAPIEN aims to enhance our capacity for communication, empathy, and understanding while prioritizing user safety and ethical considerations. This includes not retaining memory of previous interactions, limiting conversations to a 10-minute timeframe with an 8-minute warning, and allowing virtual agents to terminate calls if desired. While many focus on the hypothetical scenario of AI replacing humans, this project achieves the opposite by promoting human skills and making humans more human. This project highlights the potential of Large Language Models and human-computer interaction, setting a new standard for virtual human-based learning and communication development.